
Honeypots: Digital Honey for Hungry Hackers
A few months ago, I decided to change my VPS server. My old server had become too small, and upgrading it was no longer cost-effective compared to moving to a new instance with better specifications.
Once the operation was complete, I wondered what I should do with the old server (especially since I had paid for its renewal until August 7, 2026). I needed to find a short-lived project to deploy—a temporary service.
That’s when I got the idea to install a honeypot , a passive cybersecurity tool that remains largely unknown outside of cybersecurity circles. But what exactly is a honeypot, what is it used for, and why would I need one? That’s what we’ll explore in this article.
A Well-Sweetened Honeypot
A honeypot is a decoy deliberately placed on a network to attract malicious hackers. They believe they’ve found a vulnerability or an easy target, but in reality, we’re the ones watching them savor this precious nectar.
There are many open-source honeypots that can be installed quite easily. For this example, I chose T-Pot, an open-source solution maintained by Deutsche Telekom. It’s not just a simple honeypot, but a complete platform that relies on Docker to run around a dozen services simultaneously. It brings together several types of sensors and analysis tools in a single environment that’s easy to deploy.
The technical value lies in three main pillars, which can be summarized in the following sections.
Active Monitoring
In a traditional network, distinguishing legitimate traffic from an attack can become complex. With a honeypot, it’s different: no one is supposed to know that server exists. As a result, any connection attempt is suspicious by default.
Information Gathering
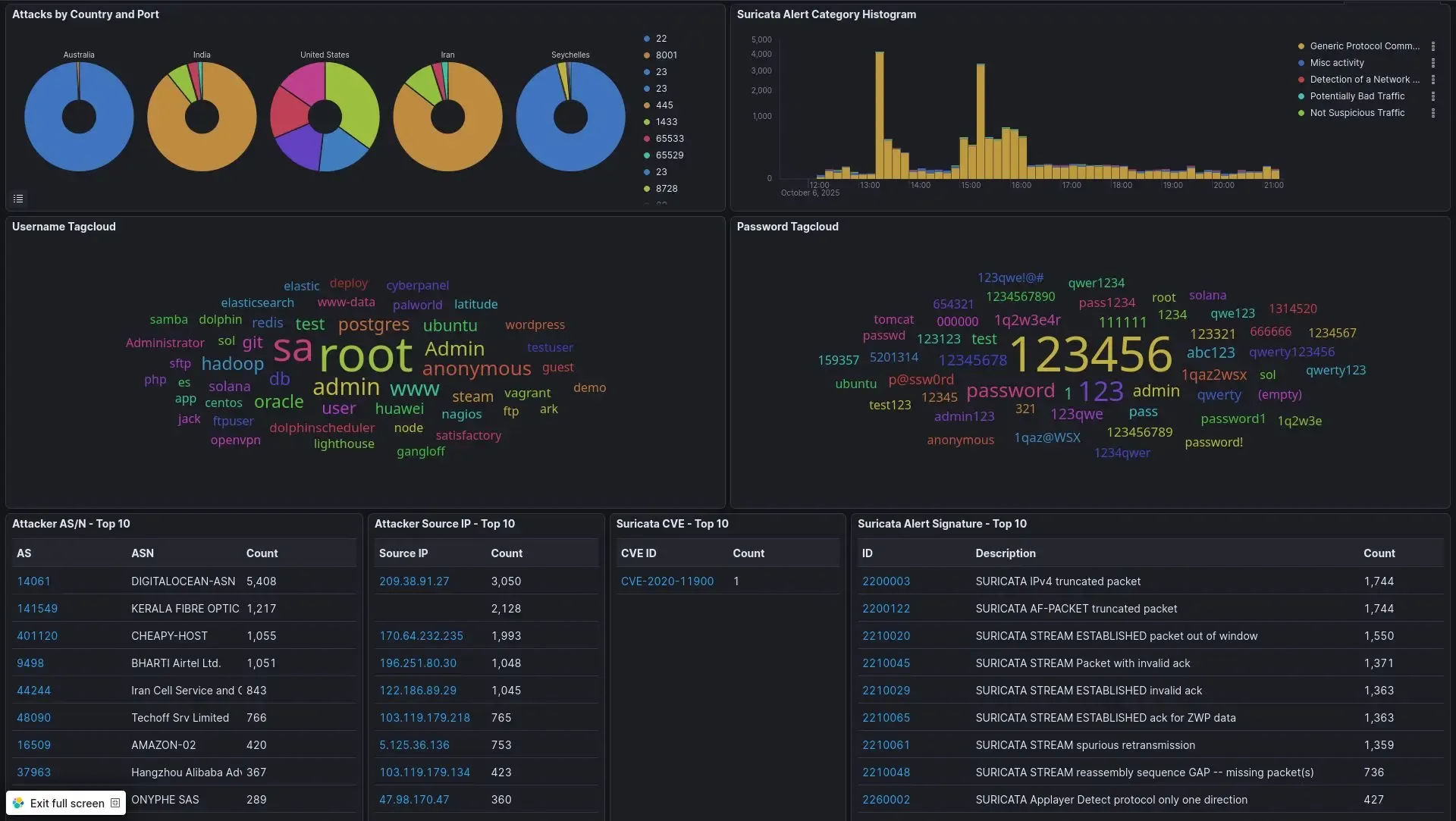
The honeypot doesn’t just act as a decoy. It simulates vulnerable services (SSH, FTP, industrial protocols, databases) in order to capture:
- Source IP addresses,
- Attack vectors (which vulnerabilities are being tested?),
- Payloads (the scripts or malware an attacker tries to download once “inside”).
Technique Analysis
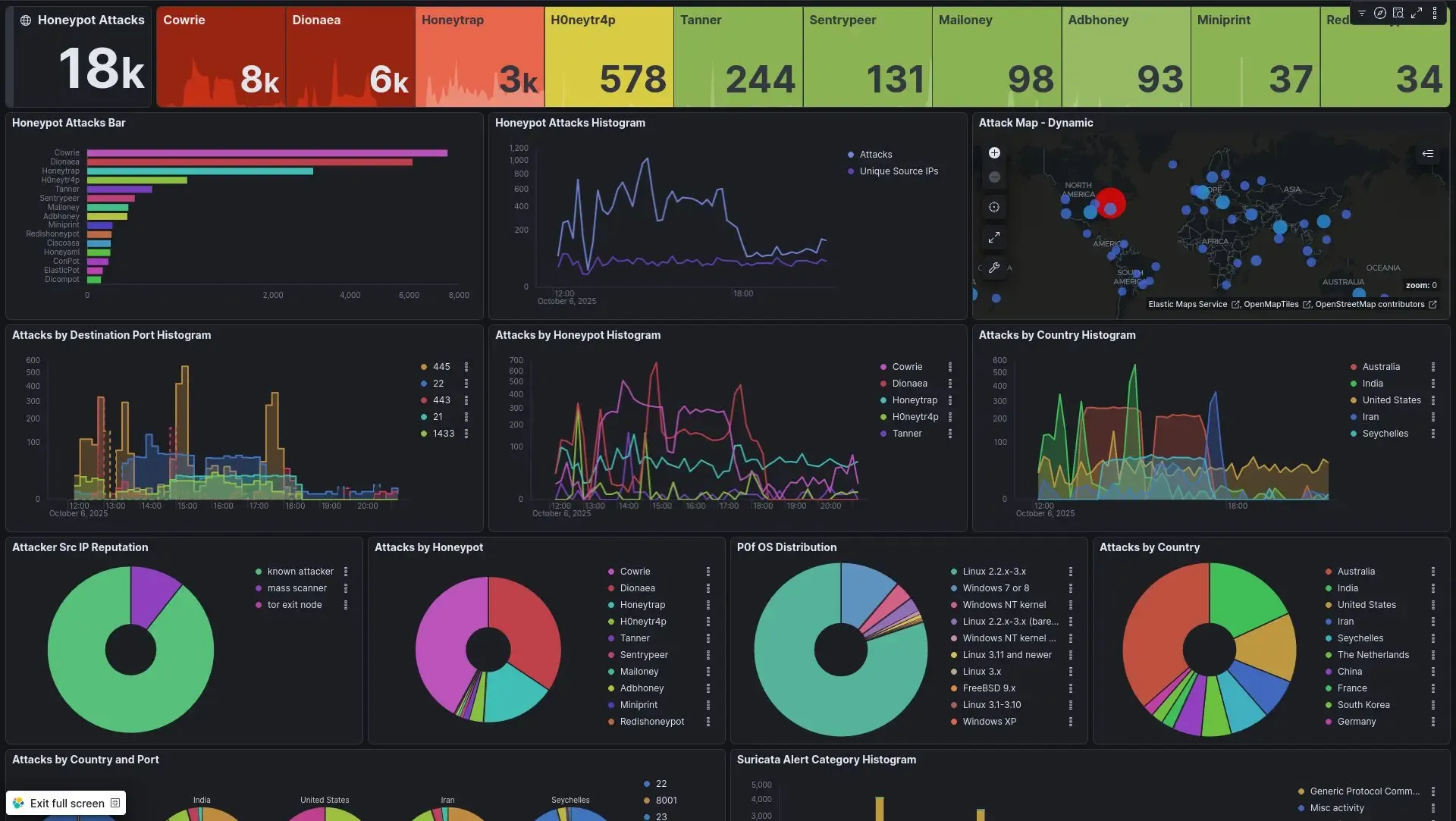
Thanks to tools integrated into the platform, such as Elasticsearch and Kibana, data can be correlated. We can analyze the techniques being used and adapt cyber defense accordingly. This is what’s known as Threat Intelligence .
Bees with a Big Appetite
In short, a honeypot is a bit like a mirror: it reflects the methods used by attackers and helps anticipate their next moves.
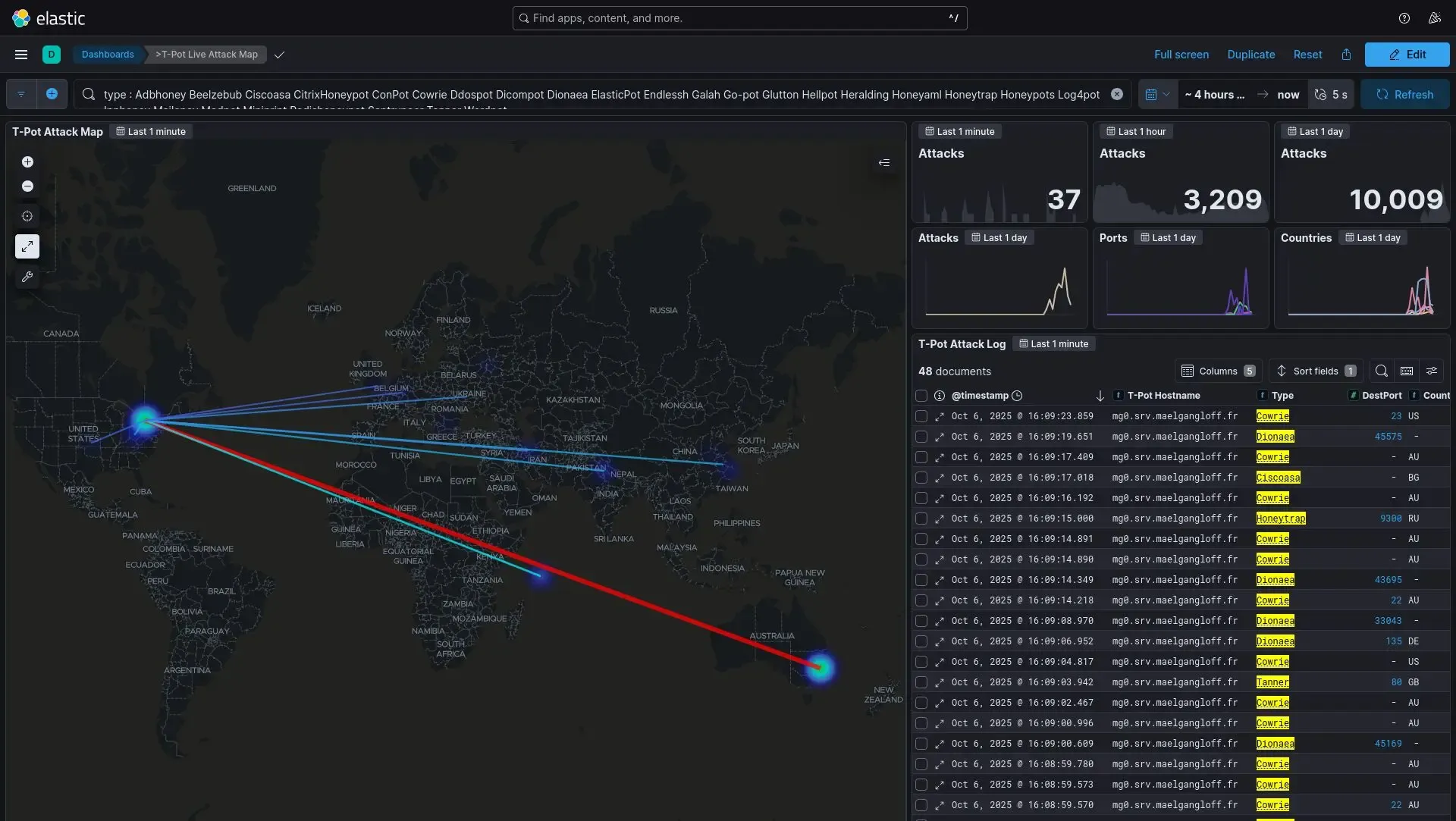
Once T-Pot was launched on my VPS, the results were immediate. Within just a few hours, the “bees” (automated scanners and bots) began swarming the server.
In an Enterprise Environment
While my experience on a personal VPS is purely anecdotal, the use of honeypots in a corporate environment takes on a strategic dimension. This is referred to as Deception technology .
Detecting Lateral Movement
In a company, the honeypot isn’t necessarily exposed to the Internet. It can be placed inside the local network (LAN). If an internal device is compromised and an attacker begins scanning the internal network to find other servers, they will eventually run into the honeypot. Since this server has no business function, the alert is highly reliable: an intrusion is underway.
Necessary Precautions
Be careful, though: deploying a honeypot requires some rigor.
- Isolation: It must be strictly isolated (via a DMZ or firewall rules) so that an attacker cannot use it as a “pivot” to attack the rest of your infrastructure—which would obviously be counterproductive.
- Maintenance: Like any server, it requires regular updates, and teams need to be trained on how to use it.
Note: Check your VPS provider’s Terms of Service before deploying a honeypot, as some providers may flag the high volume of malicious incoming traffic as a security risk to their network.
Conclusion
When I look at the statistics on the dashboard, I am amazed by the number of attacks attempted in just a few hours of service: more than 18,000 intrusion attempts from machines spread across the four corners of the world.
Installing a honeypot on my old server turned an otherwise useless resource into a fascinating window into malicious activity on the web. For the price of a small VPS, I now have access to real-world data on the current threat landscape.
If you have an unused server, installing a honeypot is an excellent way to build skills and discover a passive cyber-defense tool.
Illustration designed by Freepik
